IBC, a Gold Member of the International Precious Metals Institute, is the global leader in green refining and recycling of precious metals.
Platinum Group Metals (PGM)
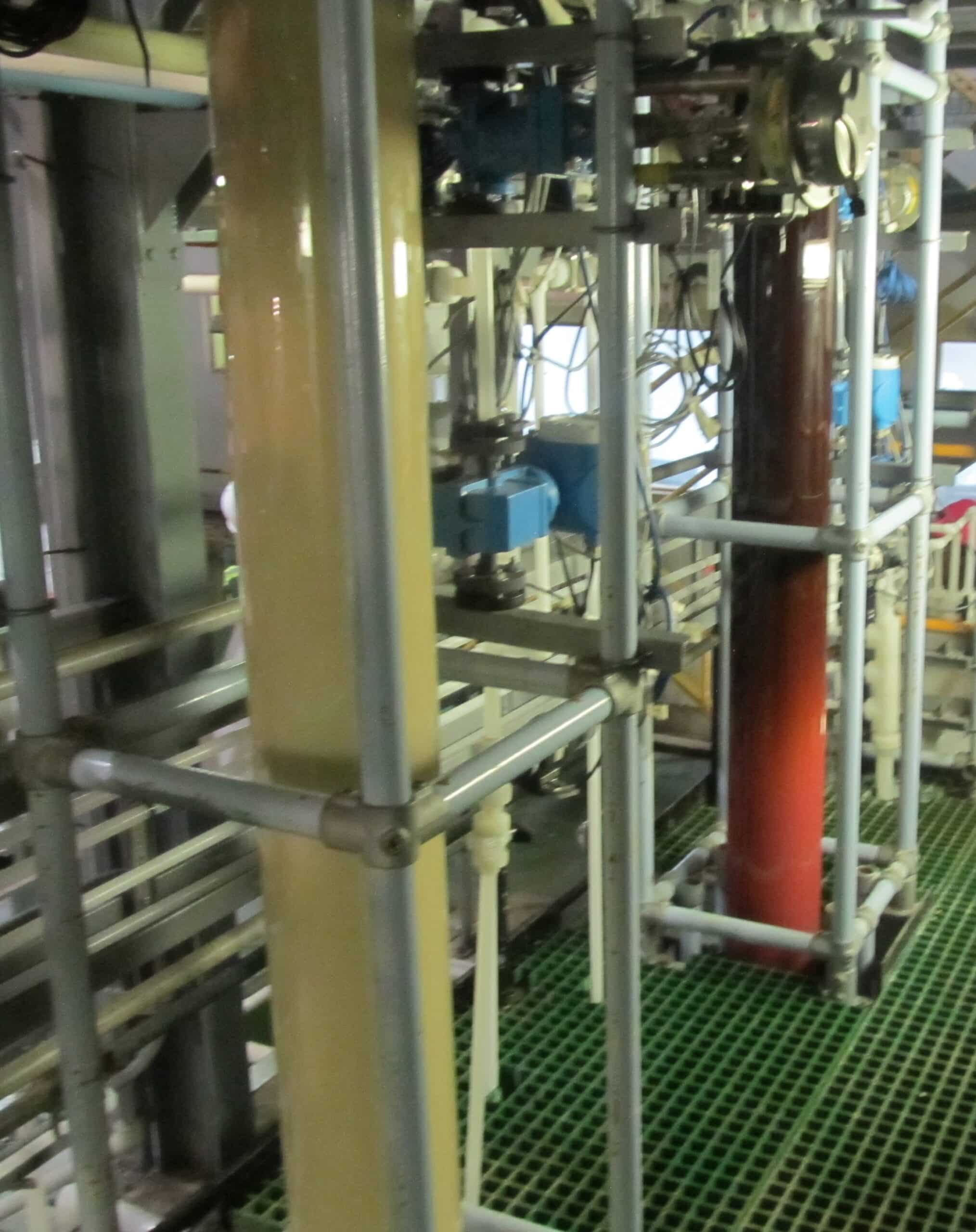
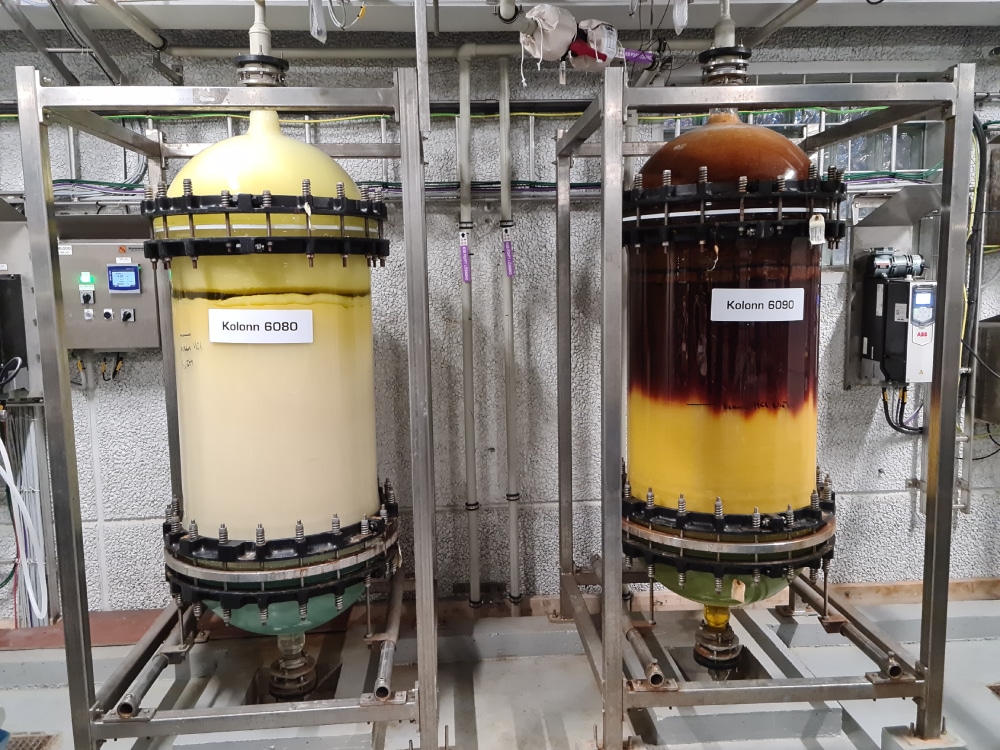
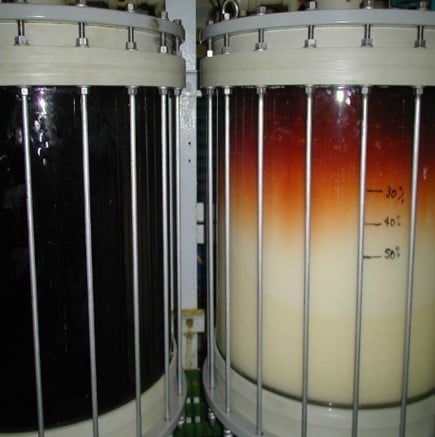
Beginning with rhodium refining from spent autocatalysts at Tanaka and palladium refining from primary ore at Impala in the mid-1990s, SuperLig® MRT™ systems have been installed worldwide at major primary and secondary precious metals refining operations for individual platinum group metal separations including rhodium, palladium, platinum, iridium, and ruthenium.
Advantages of MRT™ in Platinum Group Metals Refining include:
- Highly selective single-pass separations of 99%+ with product purities of 99.95 - 99.99%
- Green process chemistry with minimal waste, no chloroplatinate generation and minimization of platinosis
- Significant reduction in refining steps, process chemicals, and operational costs
- Shorter processing time resulting in low metal financing costs and rapid release of metal for sale
- Early flowsheet targeting of high-value platinum group metals such as rhodium and palladium
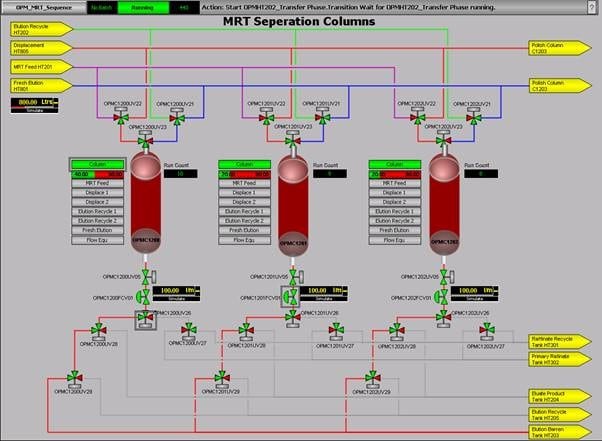
- Efficient, rapid, and semi-continuous separation process that may be automated
- Multi-cycle use of SuperLig® resins
- High throughput with compact systems that reduce CAPEX and OPEX
More benefits of MRT™ for the extraction of platinum group metals are discussed in our paper: Precious Metal Separation and Recovery from Primary and Secondary Sources using SuperLig® Molecular Recognition Technology (MRT) Processes.
Analysis of cost metrics for MRT™ and classical methods for platinum group metal refining show that MRT™ systems have superior performance with reduced Capex and Opex values compared to classical methods.
Applications of MRT™ in Platinum Group Metal Separations
MRT™ has been widely used for platinum group metals refining from both primary and secondary sources. Examples of the application of MRT™ to platinum group metals refining include:
- Extraction of platinum group metals from primary ores
- Recycling and recovery of platinum group metals from e-waste and industrial residues
- Platinum group metal separations from spent catalysts in the automotive and chemical industries
Request publications on various uses of MRT™ products for platinum group metals refining:
Platinum refining publications
- Platinum from spent catalytic converters
- Platinum from Pt/Cr/Co/Cu alloy scrap from a sputtering process
Palladium refining publications
- Palladium from spent catalytic converters and e-waste
- Palladium from primary mine feed
- Palladium from spent petrochemical catalysts
- Palladium from dipping bath solutions
- Palladium from plating baths
Rhodium refining publication
Iridium refining publications
Ruthenium refining publication
Case Study: Iridium, Ruthenium and Platinum Recycling
Key to sustainability in the emerging green hydrogen economy is the efficient production and recycling of membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), which are used for the electrolysis of water and contain iridium, ruthenium and platinum as catalysts.
Isondo Precious Metals has announced the selection of MRT™ for recycling of iridium, ruthenium and platinum from their planned production of Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEA) in South Africa.
Case Study: Iridium Refining from Primary Ore
An automated SuperLig® MRT™ refining system for iridium from primary ore has been operating at Sibanye-Stillwater’s South African Precious Metals Refinery since 2015. The MRT™ process is efficient and highly selective for iridium over rhodium.
Case Study: Palladium from Primary and Secondary Sources
The first large-scale industrial MRT™ system for palladium refining was installed at Impala in the mid-1990s. Since then, MRT™ has been widely used for palladium refining from both primary and secondary sources. For example, a green chemistry SuperLig® MRT™ process is used for the highly selective separation of palladium from various primary and secondary sources in the precious metals plant at the Boliden Rönnskär copper smelter, a world leader in recycling metals from waste electronics. Highly efficient and rapid separation and high purity recovery of palladium results in a green, sustainable, circular economy recycling process.
Gold (Au)
SuperLig® MRT™ systems are highly efficient for the recovery and refining of gold from various refining, recycling, plating and mining feed solutions at high gold purities (99.99-99.999%.)
Applications of MRT™ for Gold Refining
- Gold Recovery from High Copper Gold Ores
- Gold Recovery from Cyanide Solutions
- Gold Recovery from Aqueous Chloride Solutions
- Recovery and Recycling of Potassium Gold Cyanide (PGC) from Spent Gold Plating Solutions
Key Advantages of MRT™ for Gold Refining
- 99.99–99.999% gold purity with high recovery rates
- Compatibility with cyanide recycling for reduced reagent use
- Elimination of full refining steps for certain feedstocks
- Efficient processing of both high- and low-grade feeds
Silver (Ag)
MRT™ is used to selectively extract and refine silver from cyanide leach solutions and spent industrial process solutions.
Key Advantages of MRT™ for Silver Refining
- Over 99% impurity removal in single-pass separation
- Silver purity levels up to 99.99%
- Minimal waste generation and streamlined operations
Green Chemistry
MRT™ processes adhere to the principles of green chemistry and green engineering, making it the preferred choice for sustainable precious metals refining.
- 🌱 Zero Organic Solvents – Eliminates hazardous extraction chemicals.
- ♻ Waste Reduction – Maximizes metal recovery, minimizing tailings.
- ⚡ High Energy Efficiency – Low-temperature, low-pressure operation.
- 🌎 Minimal Carbon Footprint – Supporting a greener PGM refining industry.
Expert Reviews
Ehrlich, H.V. et al. 2017. Trends in Sorption Recovery of Platinum Metals: A Critical Survey, Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 62, 1797-1818
“The most famous and successful technology for the separation of platinum metals, used at some large enterprises around the world, employs the sorbents of the SuperLig® brand produced by IBC Advanced Technologies.”
“The exact structure of these sorbents is not known; it is only known that they are chemically modified silicas containing groups that provide specific coordination binding of platinum-metal ions or, as they say, their molecular (ion) recognition.”
Yakoumis, I., Panou, M., Moschovi, A.M., Panias, D. 2021. Recovery of platinum group metals from spent automotive catalysts, Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 3, 100112
“Molecular recognition technology (MRT) seems the latest big trend in noble metals recovery, due to its time- and cost effectiveness, green technology, high purification achieved, high selectivity and scalability”
Mooiman, M.B., et al. 2016. The Precious Metals Industry: Global Challenges, Responses, and Prospects, In Metal Sustainability, Global Challenges, and Prospects, R.M. Izatt (ed.), John Wiley & Sons, New York City, NY, pp. 362-396.
“Perhaps the most significant recent advance in PGM refining has been the use of metal-selective ligands attached to a solid support, such as silica gel. The tailoring of the ligands for different precious metals allows highly selective separations from solutions containing a suite of base and precious metals.”
“Molecular Recognition Technology (MRT) has been implemented at numerous operations but, significantly, these MRT materials are now responsible for all the palladium separations at Impala Platinum’s Germiston refinery, South Africa, as well as in applications at Tanaka in Japan and at several PGM refineries in China.”